| Complexity level: | 8 |
| Project cost ($): | 20 |
| Time required: | 5 days to prepare, 10 days for science fair project |
| Material availability: | Easily found |
| Safety concerns: | none > |
Hypothesis
A higher concentration of vitamin D will help plants grow more quickly.
Overview
Vitamins and plant growth
Vitamins are important for plant growth. Vitamins are made up of organic compounds and help plants to grow by providing them with essential nutrients. Vitamins also help plants to improve their immunity against plant diseases. The type of vitamins required to enhance growth will depend on the type of plant.
Vitamin C or ascorbic acid helps to maximize the growth of plants. Plants actually require vitamin C for them to mature. Vitamin C also helps plants with the process of photosynthesis. It also helps provide the plants with protection from ultraviolet rays, and helps the plants cope with climate changes. Interestingly, it also helps reduce plant stress!
Vitamins D2 and D3 also help to enhance plant growth. Vitamin D3 helps plants to absorb calcium into the stems. It is also very useful in plants that are pruned (grown by cutting their stems to allowing the roots to grow). Vitamin D is important is helping the plant grow roots under stressful conditions.
Scientific Terms
Materials
The materials required for this science fair project:
- 30 small plastic pots
- enough soil to fill the 30 pots
- vitamin D tablets
- 10 beakers
- 1 measuring cylinder
- 50 radish seeds
- 50 green beans
- 50 chili seeds
- 1 digital weighing scale
- 1 spatula
- 1 black marker pen
- 1 long ruler
Procedure
1. For this science fair project, the independent variable is the concentration of vitamin D used to water the plants and the type of plant used – radish, green beans and chili plants. The dependent variable is the growth height of the plants. This is determined by measuring the height of the plants with a ruler. The constants (control variables) are the number of plants in the pot, the size of the pot and the amount of soil in the pot.
2. The pots are prepared by filling soil in 30 pots. The pots are labeled as radish 0 to radish 9, green bean 0 to green bean 9, and chili 0 to chili 9. Five seeds are placed in each pot according to the label on the pots. More seeds can be placed in each pot and the additional germinated plants removed on the 5th day. The pots are watered every day with tap water and the seeds are allowed to germinate over the next 5 days.
3. Ten beakers are labeled as 0 to 9. Vitamin D tablets are crushed and 0.1 gram is added to beaker 1, 0.2 gram is added to beaker 2, 0.3 gram is added to beaker 3 and so on until 0.9 gram is added to beaker 9. The beaker labeled 0 will have no vitamin D. 100ml water is then poured into each beaker and stirred with a spatula.
4. The plants are watered using the water from the beakers for the next 10 days according to the number on the beaker and on the pot. For example, the pot labeled as “chili 5” will be watered using water from beaker 5 with a vitamin D concentration of 0.5grams/100ml water.
5. After the tenth day, the height of the 5 plants in each pot is measured. The height of the 5 plants in each pot is totaled and divided by 5 to obtain the average height and.
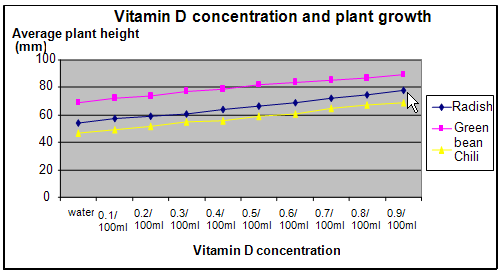
Results
The results showed that increasing the concentration of vitamin D in the water used for watering the plants, helped to increase the growth rate of the radish, green bean and chili plants.
|
Plant type |
The average height of the 5 plants in each pot after 10 days (mm) |
|||||||||
|
water |
0.1/100ml |
0.2/100ml |
0.3/100ml |
0.4/100ml |
0.5/100ml |
0.6/100ml |
0.7/100ml |
0.8/100ml |
0.9/100ml |
|
|
Radish |
54 |
57 |
59 |
61 |
64 |
66 |
69 |
72 |
75 |
78 |
|
Green bean |
69 |
72 |
74 |
77 |
79 |
82 |
84 |
85 |
87 |
89 |
|
Chili |
47 |
49 |
52 |
55 |
56 |
59 |
61 |
65 |
67 |
69 |
The graph below represents the result of our science project experiment.

Conclusion
The hypothesis that higher concentrations of vitamin D help make plants grow more quickly, has been proven to be true.
Plants normally obtain the vitamins and nutrients that they require to grow, from the soil and their surrounding environment. Fertilizers are normally added when the nutrients become lacking in the soil. Adding fertilizers definitely helps to improve the growth and health of plants.
Also consider
The science fair project can be repeated with different vitamins like vitamin C and vitamin B.
Try to repeat the science project experiment using minerals like iron, phosphorous, zinc and calcium.
References
Which vitamins help the plants to grow best? - http://www.ehow.com/list_6117470_vitamins-plant-growth-best_.html
Do plants need vitamins? - http://www.ehow.com/facts_5021521_plants-need-vitamins.html

