| Complexity level: | 6 |
| Project cost ($): | 50 |
| Time required: | 1 day to prepare, 1 hour for the science project experiment |
| Material availability: | Dominos may be purchased at a toy store |
| Safety concerns: |
Hypothesis
As the distance between the dominoes is increased, the speed of their toppling decreases.
Overview
Domino effect
Domino effect normally refers to how an action causes a similar action to occur This second reaction will trigger the next reaction and this will continue in a sequence until the last possible action has been triggered.
The simplest demonstration of this is by arranging domino tiles in a row. When the first tile is tripped, it will topple over and collide with the next tile in front of it. This will go on until the last tile has been knocked down.
No matter how long the chain of dominoes, if they are properly arranged in the first place, they will continue to topple from tile to tile, as long as the distance between the tiles is shorter than their height. Potential energy is stored in the tiles when they are made to stand upright. The energy required to topple the next domino is less than the energy involved in the collision of the tiles. The makes the entire domino effect self sustaining.
Scientific Terms
Materials
The materials required for the science fair project experiment:
- 100 domino tiles (50mm x 25mm x 6mm)
- 1 measuring tape
- 1 ruler
- 1 stopwatch
- 1 flat floor
MEL Physics — hands-on physics experiment kits delivered monthly — real experiments, not just reading. (Affiliate link)
See what’s includedProcedure
1. For this science fair project, the independent variable is the distance between the domino tiles – 10mm, 15mm, 20mm, 25mm, 30mm, 35mm, or 40mm. The dependent variable is the time taken for the 100 domino tiles to topple over. This is determined by measuring the time using a stopwatch. The constants (control variables) are the size of the domino tiles, the number of tiles used and the weight of the tiles.
2. The 100 domino tiles are arranged in a straight row. The distance between the tiles is maintained at 10mm. The total distance from the first tile to the last one will be 1584mm. As the first tile is knocked over, the stopwatch is simultaneously started. The first tile will collide with the next one, causing it to topple over. This will continue until the last tile has fallen. The stopwatch should be stopped just as the last tile falls.
3. Procedure 2 is repeated 5 times and the average time taken is calculated and recorded.
4. Procedures 2 and 3 are repeated with a distance between tiles of 15 mm, 20 mm, 25 mm, 30 mm, 35 mm and 40 mm. The average amount of time taken for the 100 tiles to topple over is calculated and recorded in the table given below.
5. The speed of the falling tiles is measured using the formulae given below :
Speed of tiles (mm/sec) = Total length of arranged tiles (mm) / Time take for all tiles to fall (seconds)
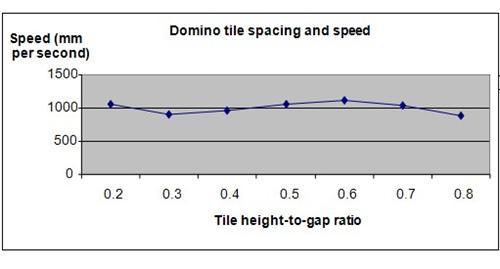
Results
It was observed that the speed of the tiles declined when the gap was increased from 10mm to 15 mm. As the distance of the gap increased from 15mm to 30mm, the speed of the tiles increased. Beyond a gap distance of 30mm, the speed of the tiles continued to decline.
|
Measure |
Spacing and speed of the 50mm tall domino tiles (millimeter per seconds) |
||||||
|
10mm |
15mm |
20mm |
25mm |
30mm |
35mm |
40mm |
|
|
Height : gap ratio |
0.2 |
0.3 |
0.4 |
0.5 |
0.6 |
0.7 |
0.8 |
|
Distance(mm) |
1584 |
2079 |
2574 |
3069 |
3564 |
4059 |
4554 |
|
Time (seconds) |
1.5 |
2.3 |
2.7 |
2.9 |
3.2 |
3.9 |
5.2 |
|
Speed (mm /sec) |
1056 |
903.9 |
953.3 |
1058.3 |
1113.8 |
1040.8 |
875.8 |
The graph below represents the results of our science project experiment.

Conclusion
Our hypothesis has been proven to be incorrect. As the distance between the dominoes is increased, the speed of their toppling decreases. In fact, the speed of the falling domino tiles only increased when the gap between the tiles was increased from 15mm to 30mm. When the gap distance was less than 15mm or greater than 30mm, the speed of their fall decreased.
More complex demonstrations using dominos have been created to demonstrate chain reactions of the domino effect. Some of the most popular ones are the Diet Coke and Mentos demonstration which can be viewed on You Tube video in the internet.
Also consider
What would happen if the science fair project was repeated by using different sizes of domino blocks or Lego blocks?
Try to repeat the science fair project by arranging 200 tiles or 300 tiles and measuring the speeds again.
References
Domino effect - http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Domino_effect
How fast do dominos fall? - http://www.utm.edu/departments/cece/cesme/PSAM/PSAM/psam15.pdf

