| Complexity level: | 8 |
| Project cost ($): | 30 |
| Time required: | It will take 3 hours to set up the science project experiment, and 2 hours to conduct it |
| Material availability: | The materials required for this science fair project can be purchased at a hardware store. |
| Safety concerns: | Basic safety requirements |
Hypothesis
The artificial mangrove swamp will absorb the impact of tsunami waves better than the man-made barrier.
Overview
Tsunami
A tsunami occurs when a series of very huge waves are generated along the ocean coastline. It is normally triggered by a violent underwater event such as a landslide, an earthquake or a volcano eruption. These events cause a large amount of ocean water displaced, triggering a tsunami.
When an underwater earthquake happens, the seafloor is suddenly becomes elevated or sinks. This causes the overlying water displaced from its state of equilibrium. The huge amount of displaced water creates waves. These waves form a tsunami.
As a tsunami approaches the shore, the sea becomes shallow, cand this in fact causes incoming waves to grow taller. Such waves can reach heights of 30 meters!. A tsunami causes a lot of damage to the shoreline. Often, many lives and properties are destroyed.
Scientific Terms
Materials
The materials required for this science project are as follows:
- a water tank of dimensions 2 meters x 1 meter x 0.3 meter
- a sand bag that weighs 3 kg
- a piece of plywood of dimension 0.6 meter x 1 meter
- a piece of plywood of dimension 1 meter x 1 meter
- a piece of plywood of dimension 1 meter x 2 mater
- enough water to fill the tank
- a box of clay or play dough
- 10 bricks
- a protractor and a ruler
Procedure
1. For this science fair project, the independent variable is the type of barrier used (a man made barrier and an artificial mangrove swamp). The dependent variable is how far the wave travels on shore. The distance that the water travels should be measured using a ruler. The constants (control variables) are the size of the water tank, the size of the sand bag, the weight of the sand bag, the slope of the shore line and the slope of the drop ramp.

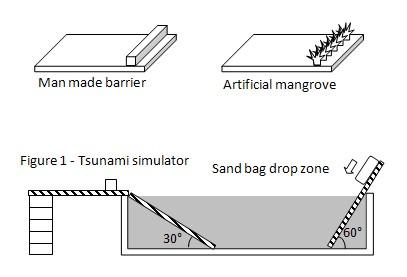
2. The tsunami simulator is set up as in figure 1. The 0.6 meter x 1 meter piece of plywood is used as the land gradient. It is tilted at 30° and fixed in place using the clay. The 1 meter x 1 meter piece of plywood is the drop ramp from which the sand bag falls. It is fixed using clay at the other end to the tank. It is tilted at 60 °.
3. The 2 meter x 1 meter piece of plywood represents the shore and inland area. The piece of plywood is supported by the water tank on one side, and by bricks on the other end.
4. The tank is filled with water until it almost overflows. The sand bag weighing 3 kilograms is dropped from the ramp. "Tidal waves" will be created. Use the ruler to measure how far the water reaches inland. The test is repeated 3 times and the distance measured is recorded in the table below.
5. The 2 meter x 1 meter piece of plywood is fixed with a man made barrier measuring 10mm tall, 5mm width and 1 meter long. The plywood is placed on the tsunami simulator and the test described in procedure 3 is repeated. The distance measured is recorded in the table below.
6. The man made barrier is removed and the plywood is fixed with some artificial plastic grass. The plywood is placed on the tsunami simulator and the test described in procedure 3 is repeated. The distance measured is recorded in the table below.
Results
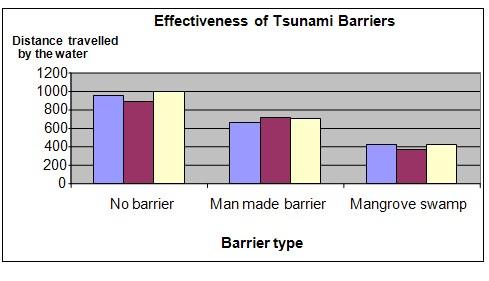
It was observed that the water traveled the shortest distance inland when the artificial grass (representing the mangrove swamp) was used.
|
Attempt |
Distance inland reached by water (mm) |
||
|
No barrier |
Man made barrier |
Mangrove swamp |
|
|
1 |
952 |
664 |
427 |
|
2 |
887 |
721 |
369 |
|
3 |
1004 |
698 |
435 |
The chart below represents the results of our experiment.

Conclusion
The hypothesis holds true: the "artificial mangrove swamp" absorbed the impact of tsunami waves more effectively than the man-made barrier.
Mangrove swamps are normally found along the coast. They are very effective in stopping the onslaught of tsunami waves. One of the first signs of a tsunami is called a drawback. This happens when the sea water recedes very significantly along the shoreline before tsunami waves are unleashed.
Also consider
Use a larger water tank that has a greater depth.
Vary the gradient of the shore.
References
About tsunami - http://www.kjc.gov.my/english/education/seismology/whatistsunami.html
Tsunami - http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tsunami#Drawback

