| Complexity level: | 7 |
| Project cost ($): | 60 |
| Time required: | 1 day for preparation, 1 day for observation |
| Material availability: | You will require transportation to the various river locations |
| Safety concerns: | Basic safety requirements |
Hypothesis
The water sample taken upstream (where there is less human activity) will contain less pollutants compared to the water sample taken downstream.
Overview
River pollution
River pollution occurs when pollutants are not removed from effluent water and are discharged into the river River water is a very important source of freshwater required to sustain life. We need a constant supply of fresh water for drinking, cooking and washing. Animals living near the river, as well as fishes and aquatic plants, also depend on clean river water.
When heavy rainfall occurs, pollutants accumulated within the boundaries of the catchment area may be washed into river channels. These pollutants include a variety of agrochemicals like fertilizers and insecticides.
Waste water containing cleaning detergents, grease and other pollutants like industrial waste may be discharged into the river channel through our drainage systems, Industrial waste may contain sulfur , thereby augmenting the acidity of the river water. Sometimes, rubbish (eg. plastic bags and bottles) are also washed into the river channel.
Scientific Terms
Materials
The materials required for this science fair project are:
- 10 empty resealable bottles
- transportation
- pH paper
- a turbidity meter
- a freshwater test kit
- 1 marker pen
Procedure
1. The independent variable for this experiement is the location at which the water sample is taken. The dependent variable is the pH reading, turbidity, ammonia content and the nitrate content of the water sample. This is determined using the pH paper, turbidity meter and the freshwater test kit. The constant(control variables) are the amount of the water in each sample.
2. The independent variable for this experiment is the location at which the water sample is taken (ie: upstream or downstream). The dependent variable is the pH reading, turbidity, ammonia content and the nitrate content of the water sample. This is determined using the pH paper, turbidity meter and the freshwater test kit. The constant (control variables) are the amount of the water in each sample, and the river from which the samples are abtained.
3. Locate a river which originates from an unpopulated hill. Ensure that downstream the river passes through, or near a town (ie: densely populated area) Collect 5 samples of the river water upstream. Use an empty bottle to do this, and label it “upstream”.
4. Collect 5 sample of the river water downstream. Use an empty bottle to do this and label it “downstream”.
5. The 10 bottles of water are then tested for their acidity using the pH paper and their turbidity is also tested using the turbidity meter. The fresh water test kit is used to test for the water’s ammonia and nitrate content. The results of the tests are recorded in the table provided below.
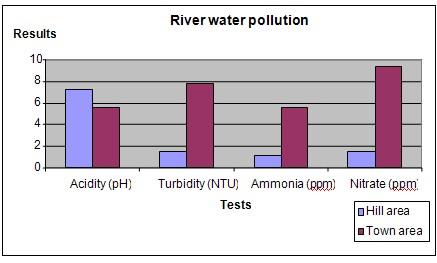
Results
The acidity of the downstream water samples is higher than that of the upstream water samples . The turbidity , ammonia content and nitrate content of the downstream water samples is also higher.
| Water samples | Tests done on water samples (Averages for each sample type) | |||
| Acidity (pH) | Turbidity (NTU) | Ammonia (ppm) | Nitrate (ppm) | |
| Upstream | 7.2 | 1.5 | 1.2 | 1.5 |
| Downstream | 5.6 | 7.8 | 5.6 | 9.3 |
Plot your results into a graph as shown below.

Conclusion
The hypothesis that a sample of river water taken upstream is less polluted than a sample of river water taken downstream is proven to be true.
Also consider
Try testing the quality of the water in lakes and ponds located at different distances from urbanized/densely populated areas.
References
Water pollution - http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Water_pollution
Common water measurements - http://ga.water.usgs.gov/edu/characteristics.html
Earth’s water- rivers and sediment - http://ga.water.usgs.gov/edu/earthriverssed.html

