| Complexity level: | 6 |
| Project cost ($): | 30 |
| Time required: | 1 day for preparation, 3 days for observation |
| Material availability: | Easily found. You can obtain most of the materials from a gardening supplies store |
| Safety concerns: | None |
Hypothesis
The runoff water of soil containing inorganic fertilizer will have the highest nitrate content.
Overview
Nitrate in fertilizers
Fertilizers are normally added to soil to increase its nutrient content and enhance plant growth. Fertilizer normally contains nitrogen, potassium, phosphorous and other micronutrients in smaller amounts. Fertilizers may be made from natural organic material, or chemically produced from inorganic materials.
Nitrogen is normally found in the form of nitrate in soil. When there is more water than the soil can hold, excess water will flow through the soil and carry the nitrates along with it. These nitrates will follow the flow of water and end up in the rivers, lakes and oceans.
The presence of nitrates in rivers and lakes encourage the growth of algae in the water. These algae reduce the level of oxygen in water and create a dead zone where fish and other water creatures cannot live and survive. The bacteria found in water will help to convert some of the nitrate in the water into nitrogen gas through a chemical process called denitrification. However, increasing levels of nitrate in the water has resulted in bacteria being able to convert only 20% to 50% of nitrates.
Scientific Terms
Materials
The materials required for this science fair project:
- 4 pots
- 4 pot trays
- Soil (enough to fill 4 pots)
- Carpet grass (enough for 4 pots)
- 1 packet of cow manure
- 1 packet of compost
- 1 bottle of liquid inorganic fertilizer
- 1 pack of granule inorganic fertilizer
- Tap water
- 1 nitrate test kit
Procedure
1. For this science fair project, the independent variable is the type of fertilizer used - cow manure, compost, liquid inorganic fertilizer and granule inorganic fertilizer. The dependent variable is the concentration of nitrate in the runoff water. This is determined by testing the water using the nitrate test kit. The constants (control variables) are the size of the pot, the amount of soil and the amount of water used for watering.
2. Label each of the 4 pots as cow manure, compost, liquid and granule. Prepare the soil for the 4 pots, as follows:
a. Cow manure – fill the pot with a mixture of cow manure and soil.
b. Compost – fill the pot is fill with a mixture of compost and soil.
c. Liquid – fill the pot with soil and pour liquid fertilizer over the soil.
d. Granule – fill the pot with a mixture of granule inorganic fertilizer and soil.
3. Plant carpet grass over the topsoil in each pot and place a pot tray under each pot. For the next 3 days, water the grass. Using the nitrate test kit, test the nitrate content in the excess runoff water in each tray. Record the results in a table, as shown below.
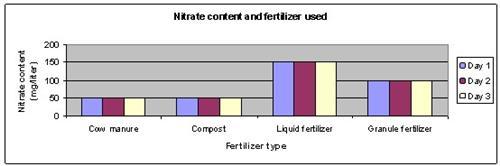
Results
It is observed that the runoff water of the pot using the inorganic fertilizer had the highest levels of nitrate.
| Day | Nitrate content in runoff water using different fertilizers ( mg/liter) | |||
| Cow manure | Compost | Liquid fertilizer | Granule fertilizer | |
| Day 1 | 50 | 50 | 150 | 100 |
| Day 2 | 50 | 50 | 150 | 100 |
| Day 3 | 50 | 50 | 150 | 100 |
The above results were then plotted onto a graph, as shown below:

Conclusion
The hypothesis that the runoff water of soil mixed with inorganic fertilizer will have highest nitrate content has been proven to be true.
The growing demand for biofuel has caused a boom in crop production and extended the use of fertilizers. Continual increased use of fertilizers is increasing the nitrate contamination of rivers and lakes and threatening the survival of fish and other living organisms. Nitrate contamination of groundwater can also cause health problems, such as the baby blue syndrome.
Also consider
The science fair project may be repeated using different type of soils like clay, sand and loam.
The science fair project may also be modified to compare the nitrate levels of different types of organic and inorganic fertilizers.
References
Fertilizer - http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fertilizer
Fertilizer runoff overwhelms streams and rivers - http://www.scientificamerican.com/article.cfm?id=fertilizer-runoff-overwhelms-streams
Selecting forms of nitrogen fertilizer - http://ohioline.osu.edu/agf-fact/0205.html

